Apparently one of the movie sensations of 2015 was Fifty Shades of Grey—a flick about the pleasure you can get from absorbing punishment. Well, I didn’t see that pile of crap myself, but I can see we have plenty of dedicated masochists in the house today…you came back after reading Part One. Good for you!
This article ain’t about making that mythical “new start” for the New Year—new starts are easy as pie. It’s keeping going that’s hard, good buddy. With that in mind, the first part of this article was about new training techniques and approaches to keep things fresh. This second half is about finding some new programming approaches to help you express freedom and creativity in your training. You’re not meant to use ALL the stuff I present to you here—just take it as the ramblings of a crazy mind. Who knows? Hopefully by the end of this article, you’ll have some fun new toys to whip out when you feel the urge.
Enough smut. Let’s go!
#1. MASTER THE SQUARE OF PROGRAMMING
I’m a big believer that athletes should develop their own programs—teach a man to fish, and all that jive, huh? With this in mind, I want to expose you to a useful bit of PCC theory we use to help coaches and trainers visualize the basics of programming.
There are four basic variables of any program:
- Mode is what you do;
- Volume is how much you do;
- Intensity is how hard you do it; and
- Frequency is how often you do it.
Imagine these four as axes on a square—the “corners” of the square being maximum (highest reps, intensity, volume, and the peak complexity/skill of the mode—e.g., compare kneeling pushups with high-skill hand-balancing):
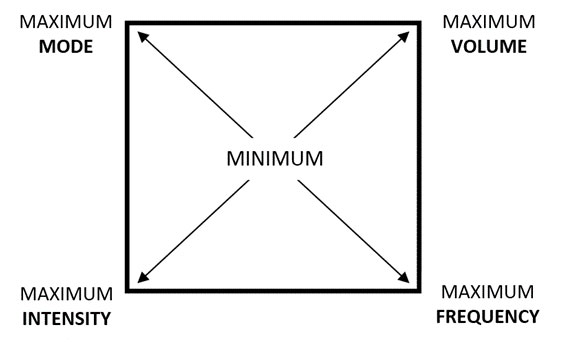
Now, in theory, any workout you care to imagine will make a pattern on this square. By visualizing different patterns, you’ll be able to understand all these four variables’ roles in a program. For example:
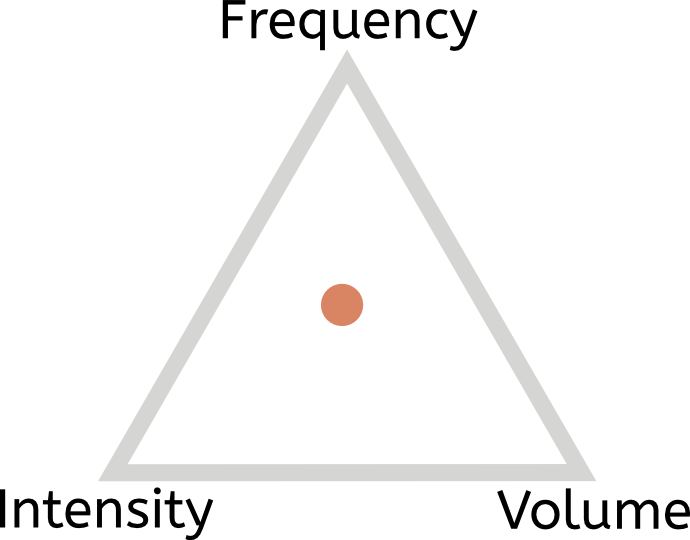
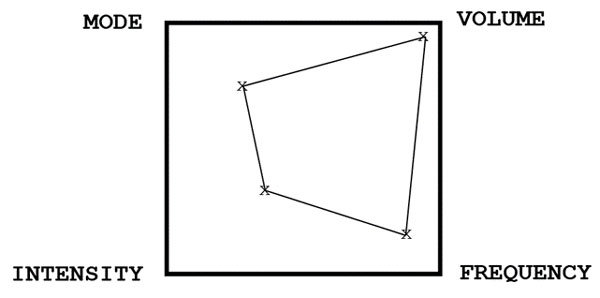
a. Injury rehabilitation
This requires lots of volume, lots of frequency, and low intensity, over very easy-skill exercises. So the square pattern might look like this:
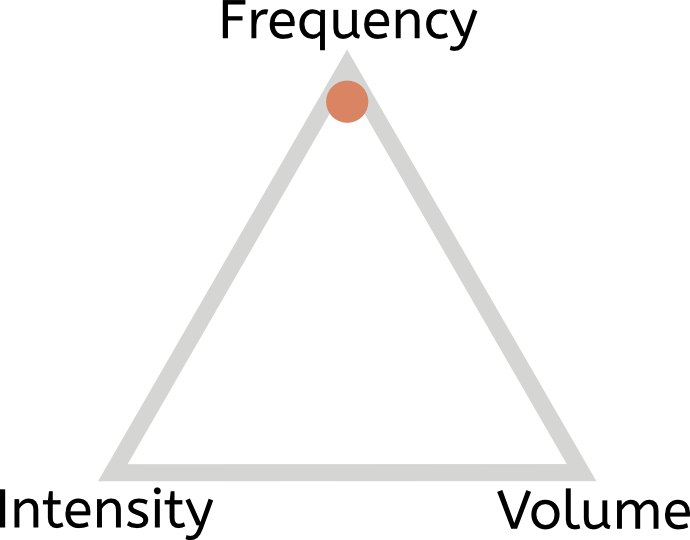
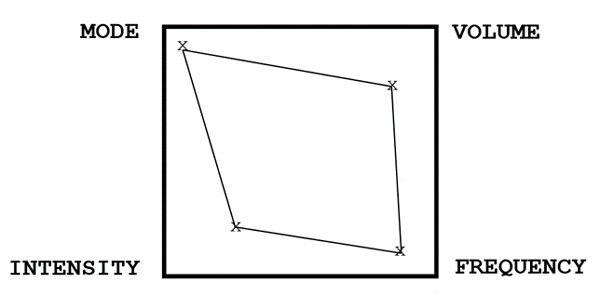
b. Skill training
Learning complex bodyweight skills—such as an elbow lever—also requires lots of practice (volume and frequency). But you should keep fresh, which means lower intensity. So the square pattern will look more like this:
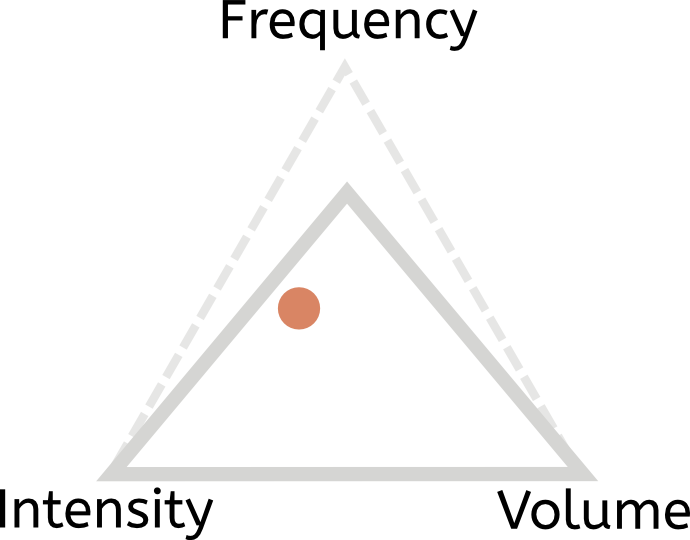
c. Hypertrophy training
The muscles need plenty of rest (low frequency) but moderate volume if they’re going to grow. You need fairly basic exercises, and you need to work them hard (intensity):
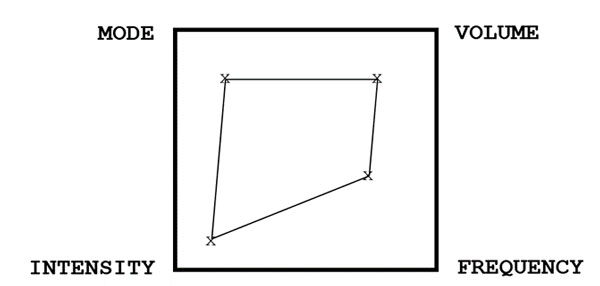
d. Strength training
Sets are moderate to high, reps are low—making the total volume somewhere in the middle. Intensity is high, exercises are big and basic:
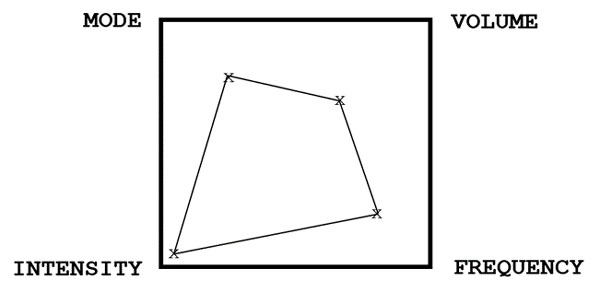
What’s that? You disagree with the data pictures in the squares? Perfect! The beauty of this approach is that you can tailor your own squares. What line graphs are to understanding and displaying economics, the square of programming is to understanding and illustrating programming theory. Think of it as a shorthand. Look at your personal goals, then see where your own workouts fall in the square.
Neat, huh?
#2. UNDERSTAND YOUR REPS!
One of the biggest favors you can do in programming your training is to understand the role that reps play. It sounds obvious, but if you want to get strong, you are going to do it more efficiently with sets consisting of low repetitions. If you want muscle growth (hypertrophy) you need more reps. For a mix of strength and size, you need somewhere in the middle. For rehab purposes—you need higher reps still
Enough jawing—a picture is worth a thousand words. Memorize this chart, then eat it.
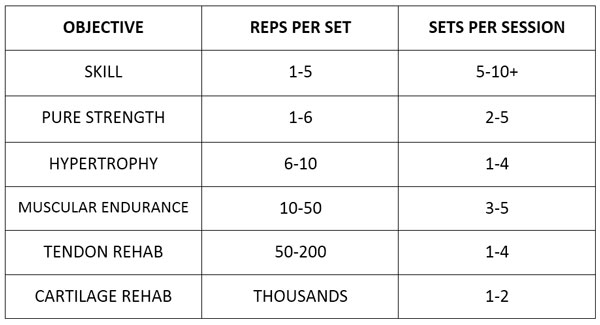
Yep, you’ll find these type of charts differ slightly. But you’re reading my article, so I guess you want my opinion on the matter. Just for you, brown eyes—in black and white.

#3. NINJA PCC STRENGTH TACTICS
I’m often asked the best way to train for strength—not mass, just strength. In the PCC Instructor’s Manual we put out eight tactics which should be considered the foundation of all strength training—honestly, I can’t put it better than I did there, so I’m going to share them with you here:
- Keep strength work brief and focused. Strength and volume are mutually exclusive. Focus on low reps, and take plenty of rest in between sets when strength training.
- Warm up. The nervous system can take time to “wake up” and generate maximum strength output. Gradually increase the difficulty of your work sets (without burn-out) during a training session to tap into your full strength potential.
- Brace yourself. The idea of “bracing” when the body is needs to exert or absorb force (the two are the same) is an ancient one. Prior to your technique—whether static or dynamic—deliberately flex all your muscles, and keep them tense as you train. This would comprise an excessive energy drain during a higher volume set (e.g., a hypertrophy set), but when applied during low-rep pure strength training it works well.
- Grip/root. Generating tension in the hands during training increases upper-body power by amplifying nerve branches running through the torso to the arms and hands. Powerlifters have used this technique for decades, gripping the bar hard during deadlifts and bench presses. Grip the bar as strongly as possible during bar work, and focus hard on “gripping” the floor with your fingers during pushups. When your feet contact the floor (e.g., squats), employ the same tactic with the feet, by generating static torque in the legs, calves and feet, and bracing the lower legs. This is called “rooting”.

- Inhale to improve leverage. Breathing in a big lungful of air prior to a positive movement can increase strength on many techniques. When the lungs are full, pressure inside the trunk increases, making the torso more “solid” as a leverage base.
- Utilize controlled exhalations. Learn to “hiss” as you exhale during negative movements. This will dramatically tighten the trunk muscles and core. Controlled exhalations can increase force production during a punch or a kick; this is why boxers and martial artists seem to hiss when they strike powerfully.
- Find your psych. High levels of strength are associated with hormones like epinephrine, which can be produced by emotional arousal. You are unlikely to see a strength record broken by a relaxed athlete—learn how to apply controlled aggression.
- Employ plyo. Explosive movements (jumps, clapping pushups/pullups) force the body to rapidly recruit huge numbers of motor units, amplifying neural facilitation. Performed before work sets, plyo temporarily raises the baseline of strength.
Expensive manuals of strength have been based around these eight simple techniques, which can double a novice’s strength in a matter of months if applied consistently. You’re welcome.
#4. 1-10-1
This is a very traditional approach to bodyweight training that’s about as old as the dinosaurs. It got popular again in the 70’s and 80’s when Arnold S. (yeah, that Arnold S.) discussed it in several training articles.
It’s a beaut for getting a lot of training under your belt on the basics like pushups, squats and pullups. Just pick an exercise you can do for over ten reps and hit it like this:
| Set # | Reps: | Set # | Reps: |
| 1 | 1 | 11 | 9 |
| 2 | 2 | 12 | 8 |
| 3 | 3 | 13 | 7 |
| 4 | 4 | 14 | 6 |
| 5 | 5 | 15 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 | 16 | 4 |
| 7 | 7 | 17 | 3 |
| 8 | 8 | 18 | 2 |
| 9 | 9 | 19 | 1 |
| 10 | 10 |
It’s a basic pyramid, allowing you to get 100 reps in total over 19 sets. Training this way has a lot of pluses: it’s high volume, and allows you to build in a lot of reps into your program without getting too fatigued; it also works great as its own warm-up. Sure, this is not the program for you if you’re on the hardcore edge of your training—trying to eke out another rep on a tough exercise, or master a new step—but it’s an excellent device to help you build on the basics. And who doesn’t need more of the basics? The basics are like exercise candy, baby!
#5. TIMED WORKOUTS—THE PRESSURE VALVE
I feel sorry for modern trainees for a lot of reasons. The prevalence of steroids and dumb expectations is one reason. The utterly mental obsession with programming is another.
I’ve been called a throwback and a Neanderthal for my programming ideas: or, to be fair, my LACK of ideas! When I started training we generally picked up a few bodyweight exercises from watching others do them, then we did them. We trained hard as we could, increased our reps and got stronger. We didn’t really talk much about programming.
Folks today are obsessed with programming. Maybe it’s the internet—I dunno. But they talk about rep ranges, cycling, periodization, percentages…Jeez, if training had been like this when I started, I might not have bothered. I wouldn’t have understood that shit!
I hear from a lot of guys in a similar position. They want to train hard—they are aching for it—but their routine is getting them down. They find it boring, constraining, being stuck in a workout rut: but they’ve expended so much time and energy working on the “perfect” program, they feel constrained to follow it.
My solution: for a few weeks, throw your program in the garbage. Seriously. Replace it with a stopwatch, and do this:
- Set yourself a fifteen-minute period every other day for training.
- Try to give yourself access to a bar, a basketball, and the floor.
- Do NOT plan your workouts hours ahead of time!!
- Take five minutes before training to put some ideas together about what to do. No more.
- Feel free to change your plan “on the fly”. Improvise.
- Do not repeat workouts. Try to keep fresh.
- Try to train as nonstop as you can for the fifteen minutes.
This is actually a surprisingly refreshing, exciting method of training. The best thing about it is that it completely removes any mental pressure than has built up, and is cramping your training. You might be thinking—fifteen minutes….damn, that ain’t long. But trust me, when you are faced with filling that time, nonstop, you’d be amazed what you can pack in there!

And what should you be looking to pack in there? This is where the creative fun starts…anything you like that’s bodyweight is game! Here are some options:
- Mobility work: twists, hamstring stretching, joint rotations, Egyptians, teacups…all groovy.
- Skill-strength work: any exercise you can barely perform for a single rep? Great! Keep returning to it during your training session!
- Pushing: pushups, jackknife pushups, chair dips, tiger bend pushups
- Pulling: Aussie pullups, pullup variations
- Cardio: Burpees, star jumps, running on the sport, jumping jacks, shadow boxing, up-and-downs—all for nice, high reps.
- Grip work: Fingertip pushups, timed hangs
- Inverse work and balances: Handstands, headstands, elbow raises, crow stands
- Leg work: Pepper in plenty! Squats, close squats, shrimp squats, lunges, broad leaps, vertical jumps, spin jumps, etc.
- Soft tissue work: any sore spots? Time to massage out the trigger points you’ve been neglecting!
See what I mean? That’s plenty to pick from right?
Don’t forget—you don’t need to stick to a strict rep range, or even a strict order. You can do ten pullups, or ten sets of one. You can do five sets of pushups, or none. You can start the session with grip work, then return to it later. It’s your call—you’re free again!
#6. THE HEAVY-LIGHT SYSTEM
You beautiful, fresh-faced hunks of gorgeousness are too young to remember, but back in the seventies and eighties, there was a war going on in gyms. Not the Cold War, or a war between Man and Machine—a war of bodybuilding styles.
In one camp were the heavy lifters. They claimed that unless you were bending bars with giant weights, and getting stronger on a diet of doubles, triples and singles, there was no way you could reach your brawny potential. On the other side were the muscle pumpers, or spinners; these guys insisted that bombing and blitzing the muscles with higher, exhausting, pumping reps was the true key to getting truly swole.
Eventually, thesis and antithesis found their synthesis, and bodybuilders began using the heavy-light routine. This involved beginning your bodypart training with the biggest weights on compound exercises you can handle. From there, you move to higher rep exercises to engorge the muscles and keep them pumped and primed. A nice solution, no?
You can also explore this general method with bodyweight training. There are several ways to go about it, but here’s what I suggest:
- Pick an exercise you can barely perform for one repetition: maybe a strict handstand pushup for shoulders. (This is the “heavy” portion.)
- After warming up, perform that technique for five single repetitions.
- Take at least a minute between reps—more if you want to.
- Now pick two pumping exercises for the same area; say, pike pushups and handstand inverse shrugs. (This is the “light” portion.)
- Perform two sets of each “pumping” exercise, aiming at 10-15 reps.
- Rest less than 30 seconds on the lighter work.
This approach might seem old-fashioned and mixed up to modern athletes—but if you can stomach it, it actually has a lot going for it. For a start, it allows you to explore your full strength potential when you’re fresh, allowing you to constantly master newer and harder bodyweight feats. (Don’t forget—you can use holds, like levers or free handstands, for the “heavy” bodyweight stuff—since it’s one rep, you don’t need to be moving.) The lighter (but harder and more painful!) work ensures that your muscle mass will always be constantly growing.

I’d advise cycling three workouts:
- Horizontal push/pull (pushup progressions, Aussie pullups or back levers)
- Lower body and abs (squats, leg raises or front levers, bridging)
- Vertical push/pull (handstand work, pullups)
This template allows for a lot of finagling—you can go three times in a row, three times a week, and so on. Give it a shot, handsome.
#7. DEFAULT MODE—CLASSIC CONVICT CONDITIONING
Most of you reading this will have a pretty good idea of what the Convict Conditioning view of sets and reps is. But a few of you won’t, which is why I want to take a moment to outline it here. Convict Conditioning is at the opposite end of skill work, and is heavily set in the muscle and strength building portion of the square of programming. There are some minor variations, but at its heart, Convict Conditioning couldn’t be simpler:
- Warm-up well with 1-4 lower intensity sets
- Perform 2 hard sets of 8-10
- Rest until recovered between sets
- Take 48 hours+ before hitting the same exercise again
- When you reach a rep target, find a way to make the exercise tougher
- Wash, rinse, repeat
This, ladies and gents, is what foolproof basic training looks like. Convict Conditioning is essentially old school, intense, power/bodybuilding-type training—which is why so many bodyweight aficionados, mired as they are in gymnastics-born systems—find it difficult to accept. Convict Conditioning is about gradually and progressively using bodyweight training as a tool to build muscle and raw strength. It is NOT about using skill-type methods to teach the nervous system into performing bodyweight “tricks”. This can be done quite quickly—but so what? If you are performing Convict Conditioning-style bodyweight work, and someone tells you to stop, because you could progress faster through the steps using skill-style or GTG training, run to the hills. They do not understand the system, nor what you are trying to achieve. It’s like a skinny guy walking into a gym and telling a bodybuilder to quit his methods and switch to Olympic lifting, cuz “you’ll be able to get a heavier clean and jerk much quicker that way”. The two are different things!

Is the Convict Conditioning way “best”…? Well, best for what? For becoming a skilled gymnast, no. For racing through progressions, no. For building a blend of muscle and strength simultaneously? Yep, I believe it IS the best. Yeah, you can apply other methods, but if you are looking for a method to use as the backbone of your training, something you return to over and over, you could do a lot worse. I say that with no ego—two hard sets and home? C’mon, I didn’t invent that shit. It’s been around since the pyramids, and will be around—and working well—long after I’m gone.
#8. SUPER HARDCORE: 5 X 5
If there’s a “classic” set and rep scheme for mass and power in the weightlifting world, this is it—the hallowed 5 x 5. 5 x 5 was heavily used and promoted by super-stud Reg Park, who was “Ah-nold’s” hero back in the fifties. Reg not only built the most badass physique on the planet (yep, he took gear—sorry but he did), he also moved more weight than Charlie Sheen has done coke, being the second man ever (after big Doug Hepburn) to bench press 500 pounds—and this was in the damn fifties, when the average man would have trouble rolling that weight.
How did he do it? He did it with his classic 5 x 5 routine: a method that became so popular, it’s still the mainstay of many hardcore routines to this day. There are many variations of this workout, but the basic one involves:
- Picking 3-5 BIG exercises—no isolation fluff!
- Perform five sets of five reps
- The first two sets should be progressive warm-ups
- The final three sets should be with the same weight: your top weight
- If you can’t get five on the last three sets, continue training with that load until you can
- When you can get five on the last three sets, jack up the load a little bit
Like most other basic approaches, this one can be stolen for bodyweight. Is it perfect? Hell no. But it’s a change, and sometimes that’s what the body—and mind—really needs.
Just pick a bodyweight strength exercise you can perform for 6-8 reps, if you’re pushing all out. Then perform two warm-up sets with easier drills (two sets of five reps) then hit your hardest exercise for three sets of five. Like Park said—if you can’t get fives on the last three sets, stick with that exercise. If you can get the three sets of five, move to a harder variation. Do this for a few of the big exercises—pushups, pullups, squats, handstand pushups—and you have a serious strength and size workout on your hands.
The trickiest part of repurposing weights programs for bodyweight use is having enough progressions at your fingertips. When you want to move forward with a barbell, you can just slap five pounds on the bar and repeat. But with bodyweight, you need to be more subtle. Tiny progressions can be made, however, if you have the right knowledge—the “hidden steps” as I can them. Slight shifts in hand or foot position; limb alignments; different body angles; depth changes. This was the real reason that I worked on the Progressive Calisthenics Certification with John Du Cane and Al Kavadlo. I wanted to create an entire generation of super-bodyweight trainers and coaches, with a toolbox of progressions so vast, that any programming method would become possible!
Don’t ever listen to goofballs who tell you that you need to use “special” programming approaches for bodyweight. It’s not true—whether you are performing dumbbell bench presses or one-arm pushups, your muscles have no idea whether you are performing calisthenics or hoisting a bar. They only contract and relax—that’s it. They don’t go onto Reddit to discuss the nuances of their day. If a collection of sets and reps works for weight-training, it will, under most circumstances, work for bodyweight!
#9. HUNDRED REP SETS?
Let’s face it—if you were to look at the rep ranges of the average calisthenics athlete throughout their career, you’d be faced with a mind-blowing level of tedium. What’s your favorite rep range? 6-8? 8-12? Truth is, we’re creatures of habit. Once we find rep ranges we like, we usually stick with ‘em. That’s no bad thing: until we get bored.
Let’s change things up. Kiss them single and double digits goodbye, and let’s go triple. You haven’t lived unless you’ve performed a hundred reps straight on a calisthenics exercise:
| Set # | Reps: |
| 1 | 100 |
The method couldn’t be simpler. Grind away at an exercise until you hit a hundred. Probably best not to start with pushups though—unless your last name is Kavadlo.
https://youtu.be/9GL17uq_tB4
If you’re new to this method, start with light stuff—kneeling pushups, half squats. You’ll be amazed at the feeling these “easy” exercises give you in your muscles. As well as enjoying the burn, you should savor these high-rep delicacies, knowing that you are building your circulation, lactic acid/waste removal systems, releasing endorphins and natural analgesics, nourishing the joints and basically just being cool as f**k.
As you gain in strength and stamina, every dedicated athlete should aspire to this kind of level:
- Close squats x 100
- Pushups x 100
- High incline pulls x 100
What? You want to do them all in one session? God damn, you stud! What a workout! Let me know how it feels to be awesome!
#10. ABBREVIATE TO ACCUMULATE
Human instinct is to overcomplicate anything we think about a lot. Unfortunately, the Golden Truth of programming is the opposite of this—if in doubt, simplify.
I recently read a program designed for the absolute beginner who wanted to get as big and strong as possible. I couldn’t believe it—there were about twenty exercises over three workouts! There were flyes and lateral raises, machine movements, this and that. You’ve probably seen similar routines yourself.
This is totally wrong. Getting big and strong—quick—is like beating someone up. If you really want to destroy someone, don’t hit them all over their body, in dozens of places. Pick only a small number of places and pound them there—over and over and over again. It’s the Principle of Concentrated Energy. This is Sun Tzu, Von Clausewitz shit I’m giving you here, son!

Those of you (the smart ones) familiar with my training philosophy will know this already, but it bears repeating. To get bigger and stronger, cut back. Cut back your exercises and your sets. You only have so much energy—neural energy, muscular energy, hormonal energy. You need to pour that energy where it counts: the big efforts on the big exercises. It’s pure Pareto Principle: 80% of your gains come from 20% of what you do. So put everything you can into that 20%!
If you are deadly serious about just getting as big and strong in calisthenics as fast as possible, do this:
- Pick three movement types: a vertical push (the pushup family), a vertical pull (the pullup family) and a lower body move (the squat family)
- Begin with fairly easy versions of the exercises to learn form, condition your joints and build psychological momentum
- After a light warm up, perform two hard work sets
- Work hard to build reps—while keeping your form pure. The harder you work, the faster you will progress
- Every time you meet a rep goal, move up to a slightly harder exercise (use the rep targets and progressions in Convict Conditioning)
Progressive bodyweight training really is as simple as that. Why do we constantly wring our hands over it, and overcomplicate it? You could write that shit on a match box.
At first—when the exercises are easy—you should be able to perform all three exercises per session; either three days per week (Monday, Wednesday, Friday) or on alternate days. As you get stronger and it takes longer to recover, take two days off between workouts. When progress slows down again, think about performing pushups on day one, squats on day two, pullups on day three, and repeating on a six-day cycle, with one day off each week.
One final tip—if you are really serious about jacking up your strength—emotional and physical—in 2016, grab hold of my favorite strength book: Strength Rules by Danny Kavadlo. I don’t get paid a red cent for promoting his book, but I’d be dishonest if I didn’t tell you this book is awesome. I learned a huge amount from it. Get it and build your year around it. You can thank me in 2017!
#11. BODYBUILDING: “GOLDEN AGE” PROGRAMS
One of the less fashionable ways to use bodyweight nowadays is by applying a bodybuilding template. Why? Because the idea of bodybuilding—isolating different muscles—is seen as very dysfunctional. Calisthenics naturally lends itself to total body training. But you know what? Screw being hip—let’s do it!
One of the classic bodybuilding programs is the old three days on: push, pull, lower body. On push and pull, you’re going to be working 3 different movement-types during each session; four, for lower body:
A. PUSH:
Horizontal pushes (pushup variations, elbow levers)
Vertical pushes (handstand pushups, handstands)
Triceps work (bodyweight extensions, tiger bends, dips)
B. LOWER BODY: Squat progressions
Squat progressions
Bridge progressions
Leg raise progressions
Bodyweight calf work (one-leg raises, jumps, etc.)
C. PULL:
Horizontal pulls (Aussie pullups, front lever work)
Vertical pulls (Pullup progressions)
Biceps work (close pullups, supinated Aussie pullups, etc.)
This is another template that stands a lot of tweaking. In the sixties, the big bodybuilders would generally do this three-session cycle over three days (Mon to Wed), really hitting their heaviest weights and busting ass. Over the next three days (Thu to Sat) they’d repeat the cycle with somewhat lighter days, taking Sunday off completely to recharge for the next week. Hardgainers can still follow the routine, but doing the three days over Monday, Wednesday and Friday, rather than twice per week. Most drug-free bodybuilders fall somewhere in the middle, perhaps taking a day off after leg day and before the next cycle, thus spreading the three workouts over five days rather than three or seven.

In my humble opinion, an even better way to work the three-day cycle is to mix up the upper-body work: swap biceps to the push day, and triceps to the pull day. Why? Well, for starters small muscle groups like arms can be worked more frequently and still grow. But the most important reason is intensity: after pushups and handstand work, most athlete find it impossible to give their triceps a damn good beating. But after pullups? Triceps are still fresh for the slaughter. Same principle for biceps. Check it:
A. UPPER-BODY I:
Horizontal pushes (pushup variations, elbow levers)
Vertical pushes (handstand pushups, handstands)
Biceps work (close pullups, supinated Aussie pullups, etc.)
Hanging forearm drills
B. LOWER BODY:
Squat progressions
Bridge progressions
Leg raise progressions
Bodyweight calf work (one-leg raises, jumps, etc.)
C. UPPER-BODY II:
Horizontal pulls (Aussie pullups, front lever work)
Vertical pulls (Pullup progressions)
Triceps work (bodyweight extensions, tiger bends, dips)
Fingertip pushup drills
The best way to hit this for most athletes?
DAY 1: PUSH/BICEPS
DAY 2: LOWER BODY
DAY 3: OFF
DAY 4: PULL/TRICEPS
DAY 5: OFF
Like I said before—this isn’t set in stone. No programming is. You can skip the rest days if you’re raring to go, or add in more if you are always sore/not recovering. Nothing bugs me more than coaches who say; use my program as it is, or not at all…don’t change a thing! Athletes are not retards. They are individuals, with brains. If they don’t have ideas, experiment and start working stuff out for themselves, they’ll never learn what works for them. They’ll always be dependent on external “experts”.
Still, I guess that works well for the experts, right?
#12. WE COULD TAKE IN AN OLD STEVE REEVES MOVIE…?
Back in his day—the drug-free forties and fifties—Steve Reeves was the greatest bodybuilder in the world. His physique was so impressive—previously unheard of mass, combined with classical lines—that it led him to Europe and made him, for a brief time, the highest paid movie star in the world.
https://youtu.be/nisz2sMQ6d8
Reeves built the bulk of his muscle on plain vanilla training: the whole body done a deal three times per week, with just one working set. Yep, Reeves used weights, but it doesn’t mean we can’t rip off his template and apply it to bodyweight training:
- Burpees: 20 reps
- Australian pullups: 10 reps
- Jackknife pushups: 10 reps
- Jackknife pullups: 10 reps
- Pushups between chairs: 10 reps
- Close squats: 15 reps
- Bridge pushups: 10 reps
- One-leg calf raise on step: 20 reps
- Incline tiger bend pushups: 10 reps
You might need to tailor this workout to meet your strength level: feel free to drop or add reps, or alter the exercises. This is just an idea, folks.
Often we make our training too complex. We overthink it. Reeve’s original-style routine is a great way to go back to basics, and get a good honest workout under our belts.
Make no mistake, this kind of template can be very powerful. Reeves himself claimed that he put on thirty pounds in his first summer of training this way! Ironically he was later disparaging of this kind of “simplistic” training, saying that he’d moved on to more sophisticated methods. Maybe that was a bad move—Steve put on thirty pounds of muscle in his first three months with this method, but didn’t gain twenty pounds over the next two decades.
So much for sophisticated!
#13. JOE HARTIGEN SETS
One of the most perfect set-and-rep schemes I ever came across was invented (or reinvented) by my mentor, Joe Hartigen. I wrote more about the Hartigen Method here, but it fits in really well in this article. It looks like this:
Warm up: with easy sets of 5 reps
| Set # | Reps: |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 |
Looks simple huh? It is!
Just pick the hardest exercise you can perform with great technique—five reps should be very close to failure. Warm up with a few easier exercises—but keep to five reps. Then, get stuck into your work sets. Do your five rep-max set, and rest for a minute or so. Now, draining as that set was, after a minute you can probably still manage four reps, right? So do it. Another minute’s rest and you can manage three, and so on—right down to one.

I love this method, which is why I’ve talked about it before. This is an elegant way to train. Unlike methods like 5 x 5 and 1-10-1, it allows you to get your hardest effort out the way immediately, and with the most efficiency.
Those of you who’d like to learn a little more about Joe’s broader training philosophy, check the article I wrote here.
#14. GERMAN VOLUME vs CALISTHENICS
This is another method drawn from the weights world—bodybuilding specifically—just to show you future greats that you don’t have to limit your mindset, just coz you are working with the greatest gym ever—the human body.
In C-MASS I discuss the difference between building strength and building mass. This confuses some folks, so I keep it stripped back: high load/tension is what builds strength. Stress/chemical drain is what builds mass. Typically, bodyweight athletes have taken their techniques from gymnastics, which is really more about building strength than mass. That’s why you have so many skinny guys performing amazing bodyweight feats. The trouble is, athletes interested in bodyweight then look at all these skinny guys and think: damn—calisthenics doesn’t build any beef at all!
Not true. You just need to apply bodybuilding methods—which drain the muscles—as opposed to gymnastics methods, which prime the nervous system.

With that in mind, here’s a classic pure mass method, straight from the Eastern Bloc. Although the name, German Volume Training, sounds kinda scientific and intimidating, this method is simpler than you might think, and actually translates effortlessly to bodyweight work. Pick an exercise you can perform 20-30 reps with, in good form. Then perform ten sets of ten reps with that exercise, with sixty second’s timed rest in between sets:
| Set # | Reps: | Set # | Reps: |
| 1 | 10 | 6 | 10 |
| 2 | 10 | 7 | 10 |
| 3 | 10 | 8 | 10 |
| 4 | 10 | 9 | 10 |
| 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
- Pick only one exercise for this method
- If you can’t make the full hundred, note your reps and try to improve each session
- Scale back your other exercises to a minimum during this protocol
- Use the method for one exercise only, twice a week
- After a month, return to regular training
I know this approach will have the low-rep skill-strength lovers pissing down their pant legs, but trust me—it works. At first, achieving the full ten sets of ten will be impossible. Your muscles will be screaming, your body pumping out more stress hormones than an actress getting a lift home with Bill Cosby. But persevere. Radical jumps of muscle size have been noted on this routine.
You’re a crazy radical, right? You’ll try something nuts once in a while? I knew it. That’s why I love ya like I do.
#15. HEAVEE DUTEE, BABEE!
In Convict Conditioning I advocate damn hard training on all work sets. I don’t however, advocate going to complete failure; I believe you should always leave a little bit of energy in your limbs in case you need them to defend yourself, or for another emergency situation. It’s how I was taught, and it’s how I teach now.
That doesn’t mean I think training to failure is a “bad” thing. It’s more like following through when you go to the bathroom; you don’t mean to do it, but sometimes you just push a little too hard. We’ve all been there. My ultimate view of training-to-failure is simple: your adaptation (how big and strong you get) is in direct proportion to the intensity of the stressor (how hard your training is). In other words, the harder you train, the better you get. Modern babble aside, everyone who has trained long-term knows this in their heart of hearts. You know it too, right?
 The king of High Intensity Training was Mike Mentzer. He shocked the training world with his one-set-to-failure philosophy, and he practiced what he preached. It was hard to argue with those results, either: back in ‘78 he was the first ever bodybuilder to win the Mr Universe with a perfect score. Many in the know also thought he was the winner of the highly controversial 1980 Mr Olympia, which was actually taken by a well out-of-shape Arnold S., who entered as a last minute contestant.
The king of High Intensity Training was Mike Mentzer. He shocked the training world with his one-set-to-failure philosophy, and he practiced what he preached. It was hard to argue with those results, either: back in ‘78 he was the first ever bodybuilder to win the Mr Universe with a perfect score. Many in the know also thought he was the winner of the highly controversial 1980 Mr Olympia, which was actually taken by a well out-of-shape Arnold S., who entered as a last minute contestant.
What would Mike make of bodyweight training? Actually, we have a pretty good idea, because his mentor—the famous Nautilus machine inventor, Arthur Jones—was, ironically a big fan of bodyweight work. He went so far as to write that pullups, dips and one-leg squats would maximize any athlete’s muscle mass.
Fancy some calisthenics, Heavy Duty style? I suggest this:
DAY 1:
Pullup progression:
8-10 strict reps (to failure)
2 forced reps
2 ten second negative reps
Handstand pushups:
to failure
DAY 2:
Squat progression:
10-15 strict reps (to failure)
2 forced reps (or self-assist)
10 reps (with an easier progression: to failure)
DAY 3: OFF
DAY 4:
Dip progression:
8-10 strict reps (to failure)
2 forced reps
2 ten second negative reps
DAY 5: Off
Repeat cycle
That was fun, eh? But screw “fun”, Paulie…is this program any good? Yes and no. If you want to ramp up your muscle and strength over ten next ten weeks, and you have a partner willing to help with the forced reps, go for it. But after ten weeks you’re gonna start dreading training. You’ll find little niggling injuries. You’ll get colds. These are all really your system’s way of avoiding the pain. For long-term results, if your training ain’t fun, it’s not gonna happen.
…Speaking of fun…
#16. ULTRAREPS: 1000 PUSHUPS IN 12 HOURS
Low reps and keeping fresh—strength as skill—is the dominating approach in bodyweight strength, and it has been in years. And there’s nothing wrong with that. It’s all a part of God’s Great Creation. Like dysentery, or pubic lice.
But let’s be honest—it’s gone too far. You’ve got athletes terrified of reps. Scared crapless of actually pushing themselves, and busting their butts on basic exercises like squats, pushups and pullups. The way some of these dudes today program, you’d think their dicks would drop off if they hit double digits on an exercise.
I’m here to tell you: that’s bullshit. There are times a man (or woman) needs to push themselves way beyond what they ever thought they could do. Doing this builds huge chemical stores in the muscles, massive stamina and intestinal fortitude.
In jail there is one bodyweight challenge which is taken very seriously indeed. The man who completes it earns instant respect as one of the true “black belts” of cell athletics. Forget singles, doubles and triples. Forget twenty rep sets. You thought a hundred reps was big boy stuff? How about a thousand reps in a single day?

It might sound impossible—and for most people, even very experienced calisthenics athletes, it is. But if you lay the groundwork and prepare for it methodically—a lot like training for a marathon—it can be achieved. You can achieve it. Before we get to anything resembling a program, here’s some Cliff Notes on the prep:
- The pushups need to be tolerable. Getting the chest 4-6 inches from the floor is acceptable, as is moving fast. Slow and controlled is great, but if you try that shit here it WILL kill you.
- Yeah, you need to get good at pushups before you do this. Unless you can do fifty reps in a regular set, don’t even think about this.
- You also need good recovery ability throughout the day. Unless five hard sets of pushups (doing double figures) is easy, keep trying until it is.
- You also need good recovery ability day-to-day just to get through this training. This is really just the result of consistent, fairly frequent training over the last few months. Unless you can perform pushup sessions with minimal soreness the next day, don’t try this at home.
Once you meet these basic criteria, you can think about beginning the real training. Obviously, a thousand pushups can’t be achieved by strength training—it’s all about stamina. The key to a successful build-up is gradually developing this stamina. If there is a “secret” to acing the 1000 Pushup Challenge, it’s this: many small drops fill the bucket. The easiest way (!) to make the grand is not by huge, mega-sets, but by lots of small sets, frequently.
Think about the math. If you woke up and tried to bust out 150 pushups straight away, you’d probably exhaust yourself for the rest of the day. But if you did two sets of twenty every half hour, over twelve hours this would equate to 960 pushups. You’d only need to make 40 before bed, and you’d hit the grand.
This is the best way to approach your conditioning. There are several ways to go about this—I’ve used and endorsed several—but here’s a good one, lasting just eight weeks:
- Strip back your other training to zero over the next eight weeks. Pushups hit the entire body; from the arms and torso to the legs, and even the toes. Don’t worry, you’re conditioning ain’t going nowhere.
- Work out every other day. (Remember—you’re building stamina here, not muscle.) Your goal is ten sets of pushups, max reps. Take two minute’s rest between sets. Constantly try to bring up your numbers through the eight weeks. Ten sets of 25 is a good start, although much higher reps are possible with time.
- One day per week, have a “test” day. On test day, you’re going to be skipping the usual ten sets, and trying to build up your stamina throughout the day. Stamina can be developed a LOT quicker than strength. Test days should build in volume like this:
WEEK 1: Perform one set of 25 every hour over ten hours (250)
WEEK 2: Perform one set of 25 every half hour for five hours (250) then every hour for the next five hours (125) (TOTAL: 375)
WEEK 3: Perform one set of 25 every half hour for seven hours (350), then every hour for the next five hours (125) (TOTAL: 475)
WEEK 4: Perform one set of 25 every half hour for ten hours (500) then every hour for two hours (50) (TOTAL: 550)
WEEK 5: Perform one set of 25 every half hour for twelve hours (600)
WEEK 6: Add a second set of 25 reps to hours 1-3 (675)
WEEK 7: Add a further second set of 25 to hours 4-6 (750)
WEEK 8: Add a final second set of 25 to hours 7-9 (825)
TEST DAY: From here, you should be good to give the challenge a try the following week. Your goal on challenge day will be to hit two sets of 20 every half hour for 12 hours—you will add a twenty-fifth session of 2 x 20, or 4 x 10—or whatever you can manage to get forty reps!—before collapsing into bed. This makes 1000.
Some final tips:
- Take two days off after every test day. You’ll need it.
- This prep is flexible. If you can’t meet the test day standards on a given week, keep training until you can.
- Take the final four days OFF before you attempt the challenge. Stretching is fine, but no pushups. This will allow your muscles to overfill their energy reserves. Don’t panic—you won’t regress.
Can you really do this?! Of course, if you want it. The body was designed to perform bodyweight exercise, and it can do better than you give it credit for. Yoshida of Japan did 10,507 pushups non-stop. You can do this, bro.
———
Phew! That’s quite a little programming journey we took there, huh? From low reps to ultrahigh reps, from strength training to pure bodybuilding, old school to bleeding-edge. Quite a little mental tour.
Was this info-dump systematic? Nope. Was it logical and consistent? Hell, no—it half the stuff in there contradicted the other half. (Like the Bible.) But that was the point of these two articles—freedom, change, variety. Acquiring ability to break off the shackles of our usual training and have the guts and motivation to try something new—trust me, that is how we keep in the game, year in, year out.
Remember, there are good routines and bad routines, but there are no perfect routines…and any calisthenics training is better than just quitting, because athletes who quit regret it down the line and wish they’d kept their hat in the ring. I guess from that perspective, “perfect” is whatever keeps you training, right?
Thanks for reading this—or skipping to the end and pretending you did. Either way, old Coach had a fine time sitting writing this for you guys and gals. I really, really hope you can take something from it that helps ya, however small. Please hit me up in the comments with any thoughts, questions, or just to say hi. I will answer all of you, and have a fantastic time doing so!
Big love again goes out to Adrienne and all the Kavadlo clan for the huge help they gave me in delivering this little ankle-biter.
***
Paul “Coach” Wade is the author of Convict Conditioning, Convict Conditioning Volume 2, the Convict Conditioning Ultimate Bodyweight Training Log, and five Convict Conditioning DVD and manual programs. Click here for more information about the Convict Conditioning DVDs and books available for purchase from Dragon Door Publications.