Men and women of all fitness levels are familiar with the push-up and its ability to challenge and build full body strength and muscle. There are many ways to regress and progress the push-up to fit the needs of any everyday athlete. Regressing the push-up’s difficulty can be as simple as changing the angle of the body or adding the use of your knees for a closer point of contact to redirect weight away from the upper body and arms. Progressing the push-up to a more advanced variation can consist of changing or removing an extremity position, adding an external resistance, and changing the angle of the body to redirect more weight into the upper body and arms. Each push-up progression delivers a unique challenge (as with most functional exercises) that can be felt throughout the arms, shoulders, chest, back, and especially the core.
 As progression remains a staple focus to any athlete’s training program, the need to challenge the body further than performing more repetitions or adding more resistance to the same exercise over and over again becomes a necessity.
As progression remains a staple focus to any athlete’s training program, the need to challenge the body further than performing more repetitions or adding more resistance to the same exercise over and over again becomes a necessity.
So we start to add variations. As your strength and ability within the push-up progresses, you will be challenged with different positions and fewer points of contact. Each variation will bring a different challenge to the body.
Some of my favorite push-progressions are explained in depth within the PCC; such as the archer push-up, the pike press, and the 1-arm push-up.
Each of these push-variations changes the body’s position, changing the way the extremities and core integrate when challenged throughout each repetition—stimulating the body’s soft tissue (muscle, ligaments, tendons, fascia, and skin) in a different way through various ranges of motion.
Anti-Rotation Variations
Standard strength training and muscle building exercises focus on performing repetitions in the sagittal plane. One way to progress an exercise in the sagittal plane is by adding a unilateral component, increasing the difficulty that is felt throughout the entire body. Some examples of unilateral variations are a 1-arm plank compared to a standard plank and a 1-arm push-up compared to a standard push-up.
Both of these unilateral variations require extreme muscular tension that originates in the deep core and radiates out through the extremities to integrate the body as one unit; this is known as bracing. Bracing improves muscular integration, muscular strength, joint stability, and joint alignment — allowing the body to fight off the external forces that want to pull your unsupported side down to the ground. When a point of contact is removed in the push-up position, bracing the entire body tight is what allows the body to remain horizontal. Fighting against the forces of gravity and resistance wanting to pull the body a certain way is known as Anti-Rotation.
Without bracing the body for anti-rotation it would be nearly impossible to remain horizontal while performing a 1-arm plank and 1-arm Push-up.
Posi-Rotation Variations
What about training the body through rotation? I would like to introduce a Posi-Rotation variation to our classic strength training exercises. Pose-Rotation variations such as the Intrinsic Strength Push-up challenge the body to maintain core tension and joint stability as the body rotates in the transverse plane while on the ground.
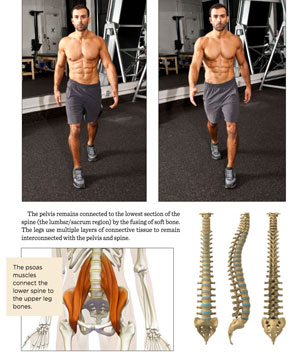 Our multifaceted, dynamic body moves in three dimensions with every step we take. The standard function of walking requires a synergistic rotation of the shoulders, spine, and hips. Whenever watching the body move, the transverse plane will always be in “plane” sight.
Our multifaceted, dynamic body moves in three dimensions with every step we take. The standard function of walking requires a synergistic rotation of the shoulders, spine, and hips. Whenever watching the body move, the transverse plane will always be in “plane” sight.
Since our spine rotates with every step that we take, All humans should be incorporating transverse plane training into their daily workouts.
Training the spine to rotate safely with control is an excellent way to stimulate the body’s ligaments, tendons, muscles, and fascia differently than a regular strict push-up.
Adding a rotational variation to this classic strength exercise will facilitate a different stimulation of soft tissue, leading to a more able body that is stronger in more positions while on the ground and standing.
As the body rotates through each repetition, the arms and shoulders have to adjust to the rotating torso – adding lots of variability throughout the entire body with different leverage points, ranges of motion, and body weight displacement.

The Intrinsic Strength Push-Up:
IST push-up variations deliver a unique challenge to any athlete from beginner to advanced. This push-up progression stimulates and strengthens the horizontal press with global rotation.
Intrinsic Strength Push-ups offer three variations to the horizontal pushing motion during the same set without having to change the position of the hands. This simple eye gaze over the right and left shoulder allows the muscles to stay engaged, providing the body with great T.U.T. ( Time Under Tension) while still delivering a variation. Improving strength and muscle throughout the chest, shoulders, back, arms and core is only possible through physical adaptation from Time Under Tension. The more time spent working the position, the more the body adapts to that position.
This horizontal rotation is performed by lowering down to the bottom of the push-up while simultaneously taking the eye’s gaze over one of the shoulders. This transverse plane variation causes the shoulders, torso, and hips to rotate to that same side, changing the weight distribution through the arms.

How To Perform the Intrinsic Strength Push-Up
- Start with your feet in a bilateral stance, shoulder width apart.
- Walk both hands out on the floor until you are in a plank position.
- While lowering down to the bottom of the first push-up, simultaneously take your gaze over your right shoulder and return to the high plank position.
- Do a regular push-up, after returning back to the high plank position
- While lowering down to the bottom of the third push-up, simultaneously take your gaze over your left shoulder and return to the high plank position.
Angelo’s Advice
- Allow every joint to help with the full body rotation.
- Your eyes will direct your head, shoulders, spine, and hips to rotate towards the same focal point (above the shoulder).
- Actively apply pressure into the ground through your legs and feet to create lower body tension.
- Actively apply pressure into the ground through your shoulders and fingers to create upper body tension.
- This extremity tension will radiate through the core – ensuring core tension and more muscular activation.
When turning the head over the right shoulder, you will notice that:
- More weight and tension will shift into the left shoulder.
- A stretch will be felt throughout the left chest
Perform a series of three push ups to complete one repetition of an IST push up.
First push-up: look over the right shoulder.
Second push-up: look in-between your hands.
Third push-up: look over left shoulder.
****
Angelo Grinceri, PCC, FAFS, is the author of Intrinsic Strength: A Breakthrough Program for Real-World Functional Strength and True Athletic Power Angelo’s fitness journey started with a focus on aesthetics and bodybuilding. As he grew as an athlete and coach he started to focus on strength training, corrective exercise, and athletic function. He realized a connection was needed between these different modalities and Intrinsic Strength Training® was born. Based in NYC, he can be contacted through his website, IntrinsicStrengthTraining.com. Follow him on Youtube, Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter for Angelo’s Advice and follow-along workouts.
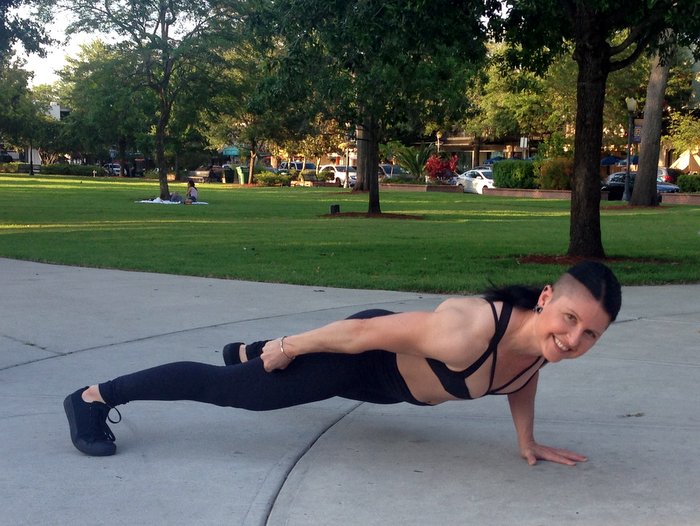
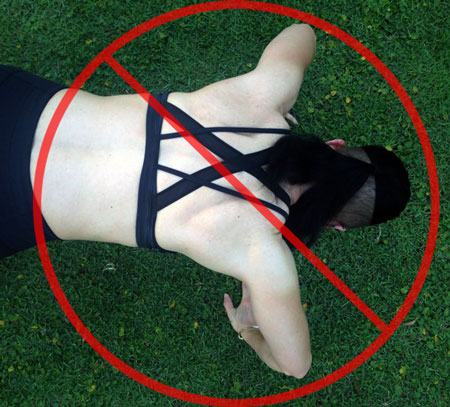
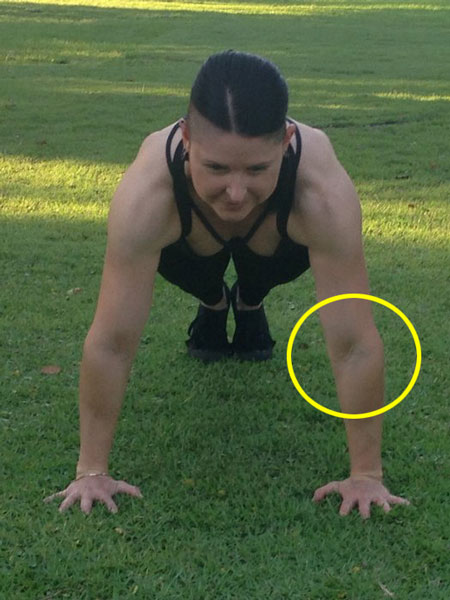
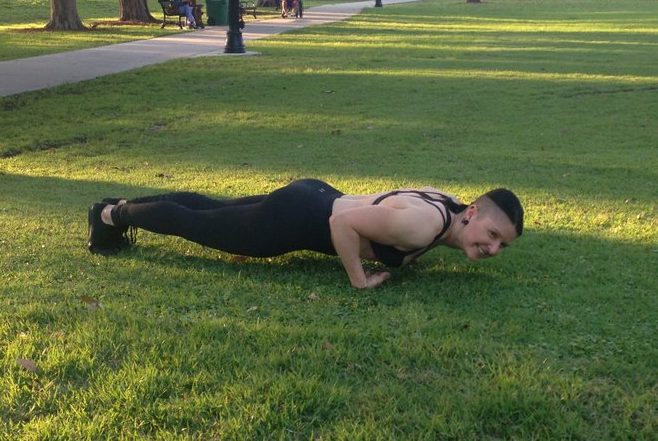
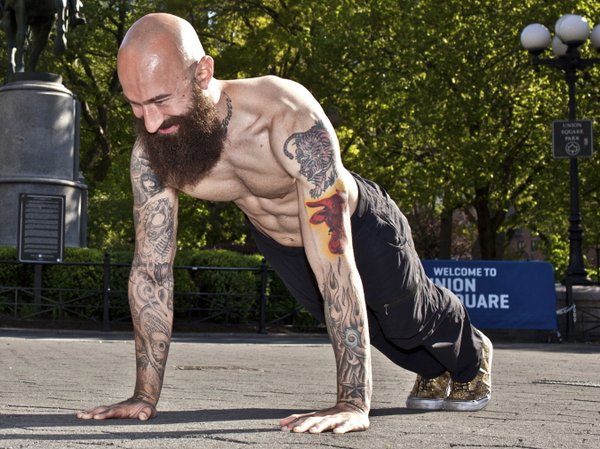
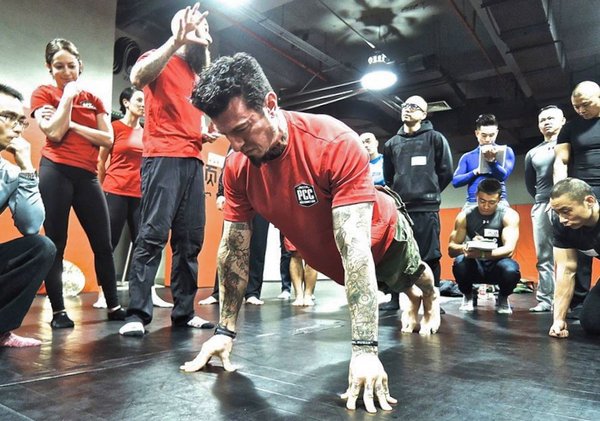
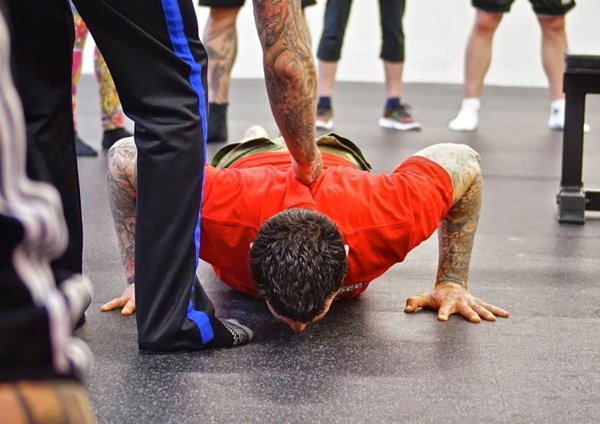
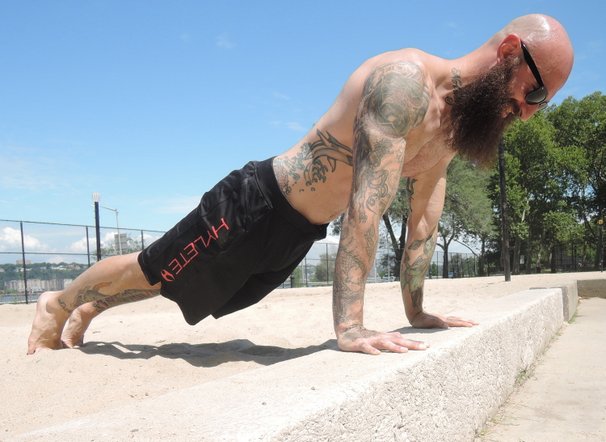







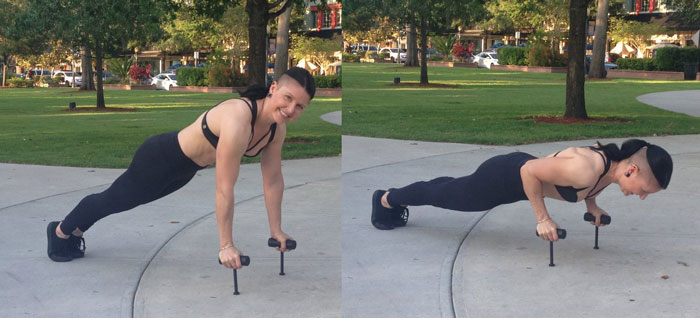







 The struggle to load the push-up…
The struggle to load the push-up…






