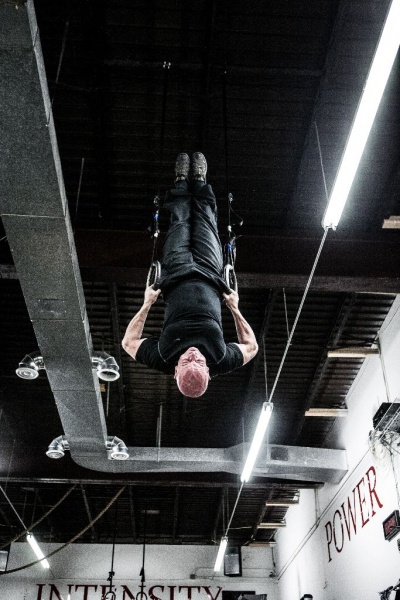
Anyone who’s familiar with extreme calisthenics already knows the infamous human flag exercise; the dragon flag variant, however, is an equally awesome move that fewer people are aware of. It looks cool, it’s commonly associated with Bruce Lee, and there’s so much that can be learned by working up to and practicing it. The other great thing about the dragon flag is that learning to do one means learning how to create an incredible amount of tension throughout your whole body—an essential skill for all advanced calisthenics. While there are many different paths to the dragon flag, the multi-faceted one shared below has worked well for a few clients and myself. Some of these drills led me to the dragon flag before I was ever really trying for it. Oddly enough, even though they require very maximal effort, I’ll usually leave dragon flags for the end of the workout, or focus on them at a separate time of day from my main workout. Regardless, it’s also a good idea to be warmed up. The Trifecta from Convict Conditioning 2 using the bridge, L-sit, and twist is a great sequence to practice before and after your calisthenics work, especially high tension moves like the dragon flag!
It seems like all forms of the flag require an extreme level of tension. Whenever I catch myself not properly respecting that fact on any flag progression, I remember watching Danny Kavadlo psych himself up for one of his human flag demonstrations—that fierce-looking (and sounding) process is nearly as impressive as the feat itself! But the good news is that since most serious bodyweight enthusiasts will naturally already have some of the requisite abdominal strength, the dragon flag may be a little bit “easier” to achieve than a full human flag. It certainly requires a little less skill since it’s usually performed on a solid bench, or from the ground with a low bar, instead of self-suspended in the air while gripping a pole!

The dragon flag can also be performed on a pole, but it requires a bit of pain tolerance (pick which trap you want to jam the side of the pole into) and extra time practicing the correct grip—plus you’ll also have to fight the rotation from that off-centered pole! For comfort and simplicity—especially at the beginning—using a bench, a well-secured very low bar, or similar set up is best for learning the dragon flag. Certain types of very simple ab stations on fit trails (look for a flat platform with a low bar attached at one end) can also be appropriate for flags, though I would recommend padding the surface under your shoulders.

For safely make sure that whatever you are using, grabbing, and pushing against is sturdy and can support your entire body weight or more.
Alternately, on a flat bench, you can choose to place your hands on the sides of the bench (usually near the ears, but everyone’s placement will be slightly different) or behind your head as shown below:

Since the dragon flag requires a lot of tension, proprioception and skill, I’ve used multiple steps and strategies to progress towards it. Many of these moves are good for warming up when you’re able to do the full flag too.
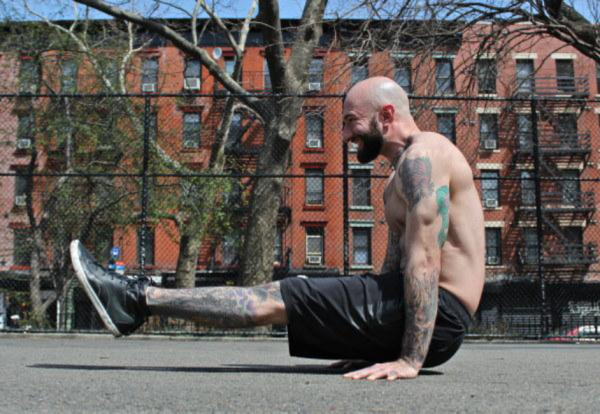
1. The “Hardstyle” plank: The ability to really own the full body tension in this intense version of the plank is crucial. To me the dragon flag feels like an extra serious, less unsupported Hardstyle plank. (Think of doing a plank on just your arms.) The Hardstyle plank differs from the regular variety because the whole body is tensed, the elbows are pulling towards the toes really engaging the abs, and the heels are pushing outwards as well. Similarly, the glutes are engaged too—as they are in the dragon flag!

2. Lying leg raises from the floor—while these are a LOT easier than a dragon flag, remaining tense with your legs just a few inches off the ground while fully engaging your abdominals will really help you towards the goal of the dragon flag.

3. A yoga-like shoulder stand—learning to balance up on your shoulders and NOT your neck will help you get into the right position at the midpoint of the dragon flag, or the starting point of the negative version. Familiarity with the feeling at this position can help insure that you’re keeping the body in a straight line as you descend, and eventually ascend too. The more balanced you can be at this midpoint, the more chance you have for a little “rest” between the grueling ascent and descent of the full dragon flag.

4. Tuck-flags or roll-ups (I’m sure someone has a better name for this drill). As we know from many other bodyweight exercises (L-sits, front and back bar levers) if we shorten the length of our legs, then the more favorable leverage makes the move much easier. While in a tuck position, use your abs to slowly pull your tucked body up off the floor onto your shoulders while firmly gripping the bench or very low bar, slowly lower back down until your abs are almost screaming! This move is not to be done quickly, and is surprisingly difficult if performed correctly—especially for reps! Gradually straighten the legs more and more to increase difficulty.

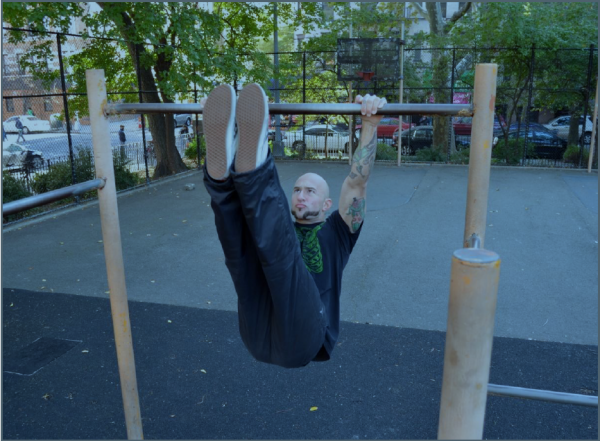
5. Negative dragon flags. Grasp the bench or very low bar and begin from the shoulder-stand-like top position. After making sure you’re resting on your shoulders, not your neck, tense the whole body (torso, glutes, legs, etc.) and try to lower yourself slowly, and under control without bending at the hips. You may feel like you’re supporting most of your body through your arms at first, but try to mitigate that feeling by really keeping the body tight during every second of your descent. This takes an amazing amount of tension. The closer your legs get to the ground, the more difficult the move becomes. Try to maintain the straight body position and the tension as long as you can without just dropping your legs at the bottom of the movement. The abs, glutes, legs and everything in between are strongly engaged (I’ve even managed to cramp up one or both feet while practicing these!)
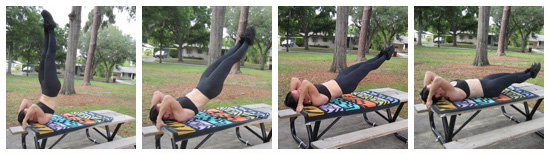
6. Full dragon flags up from the ground, towards the shoulder-stand-like position, then descending. It’s very easy to accidentally cheat these on the way up, as your hips will want to fold to help you out. Instead, think of maintaining a slightly flatter version of a hollow position while focusing on keeping the body as one solid plank. I think the most difficult part of this move is initiating the movement from the ground. The first few seconds feel nearly impossible on some days!
Steps 1-4 can be practiced together, but practicing the negative flags and full flags is incredibly taxing. I typically won’t do more than 1-2 per set for negatives, and only 1 full dragon flag per set, for a session total of 3-5 sets. That’s ten reps total for the day at most. You may be able to work up to more over time, but this move takes practice, patience, and long term dedication, so best to ease in gradually.
While some may dismiss moves like the dragon flag and human flag as “party tricks,” these very cool looking moves are rewarding to conquer as they challenge our patience along with building strength, skill, and control. Thankfully, these hard-won concepts will carry over directly and indirectly to many other bodyweight drills, skills and feats of strength.
***
About Adrienne Harvey, PCC Team Leader, RKCII, CK-FMS, Primal Move Nat’l Instructor: Originally RKC Certified in 2010, and RKC Level 2 certified in 2011, kettlebell and bodyweight training have been crucial in Adrienne’s personal quest for fitness. A core member of the PCC team, Adrienne loves sharing her knowledge with small groups and individuals. She also loves to develop recipes and workout programs to further support performance, body composition, and of course—FUN. Go to http://www.giryagirl.com for more information about Adrienne!